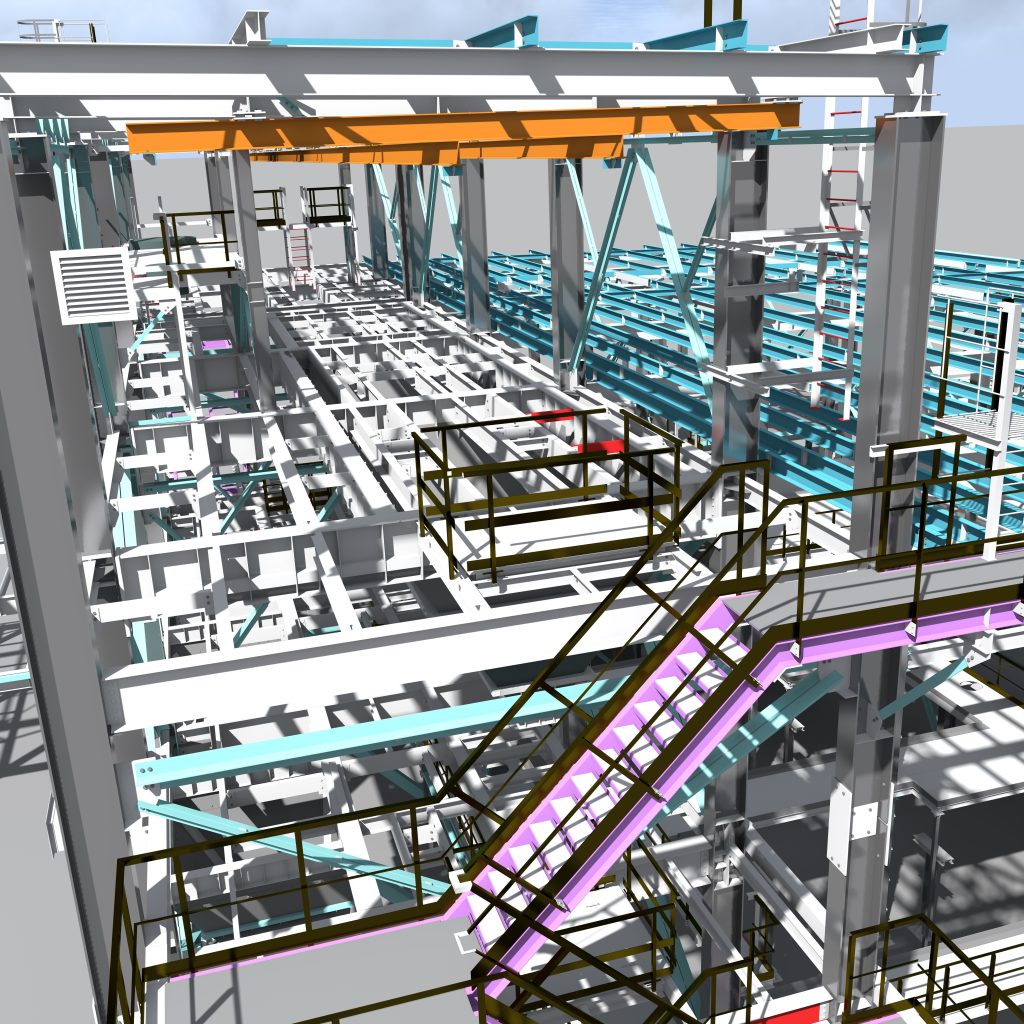
BIM
(Building Information Modeling)
BIM (Building Information Modeling) services refer to the process of creating and managing digital representations of a building or infrastructure project. BIM is a collaborative approach that integrates various aspects of a project, including design, construction, and operation, into a single digital model. BIM services encompass a range of activities and technologies aimed at improving project efficiency, coordination, and communication.
Here are some common BIM services:
BIM modeling involves creating a three-dimensional digital representation of the building or infrastructure project. This includes architectural, structural, mechanical, and electrical elements, as well as other systems and components. BIM models are typically developed using specialized software and can include detailed information about materials, quantities, and specifications.
BIM services include clash detection, which identifies potential conflicts or clashes between different building systems or components. By integrating various disciplines’ models (architectural, structural, MEP), clashes can be detected and resolved digitally before construction, reducing errors and rework during the actual construction phase.
BIM models can be used to simulate construction sequences and visualize the project’s progress over time. This helps in identifying potential construction issues, optimizing workflows, and communicating construction plans to stakeholders.
BIM services can extract accurate quantities of materials and generate cost estimates based on the information embedded in the BIM model. This helps in project cost planning, budgeting, and procurement.
BIM models can be utilized for facility management purposes, allowing for the integration of information related to equipment, maintenance schedules, and asset management. This information can be useful for facility managers during the operational phase of a building.
BIM models can be used to perform energy analysis and simulations, helping to optimize building performance and sustainability. This includes evaluating energy usage, daylighting analysis, thermal analysis, and overall building performance analysis.
BIM services facilitate collaboration among project stakeholders by providing a common platform for sharing and accessing project information. This improves communication, coordination, and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Services & Solutions
- 3D BIM Modeling
- 4D BIM Schedule
- BIM Consulting
- Cost Estimation (5D BIM)
- Facade Detailing
- Curtain Wall Detailing
- BIM Coordination
- Point Cloud Scan to BIM
- Fabrication & Shop Drawing
- Revit Family Creation
- BIM for Facility Management
- Electrical BIM Shop Drawings
- BIM for Modular Construction
- Industrial Engineering
- Virtual Design & Construction
- Solar Panel Detailing
- Digital Twins
- As Built Drawings
- Millwork Drawings
- Coordination Drawings
- BIM for Civil & Infrastructure
- Rebar Detailing
- BIM Model Audit
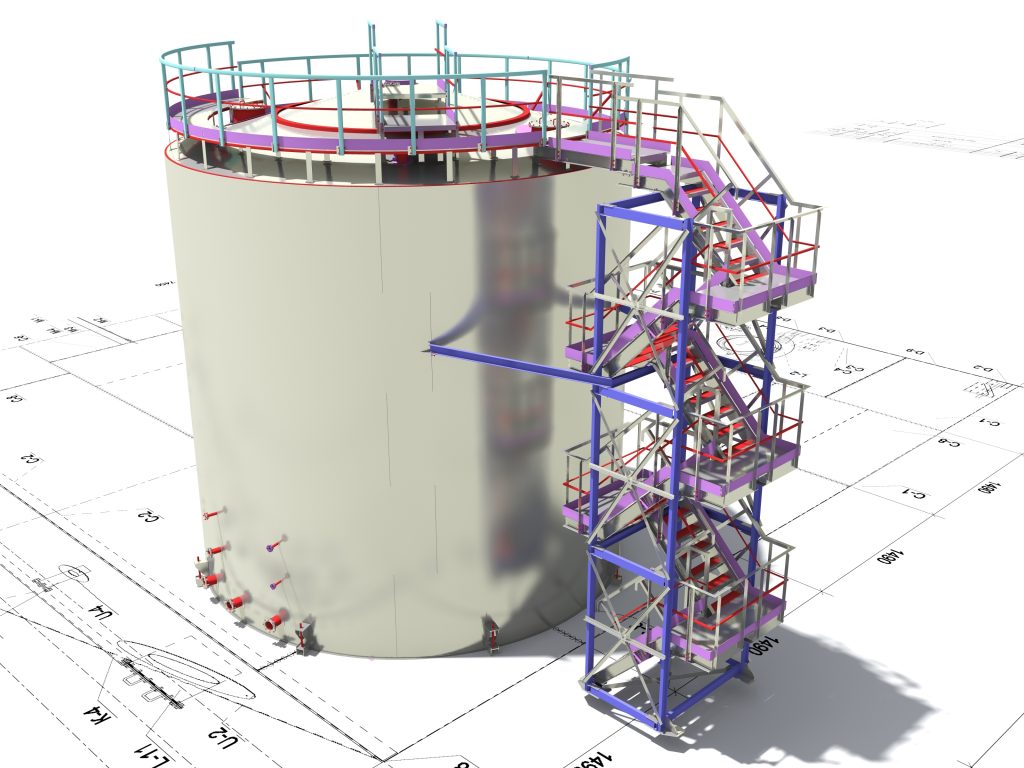
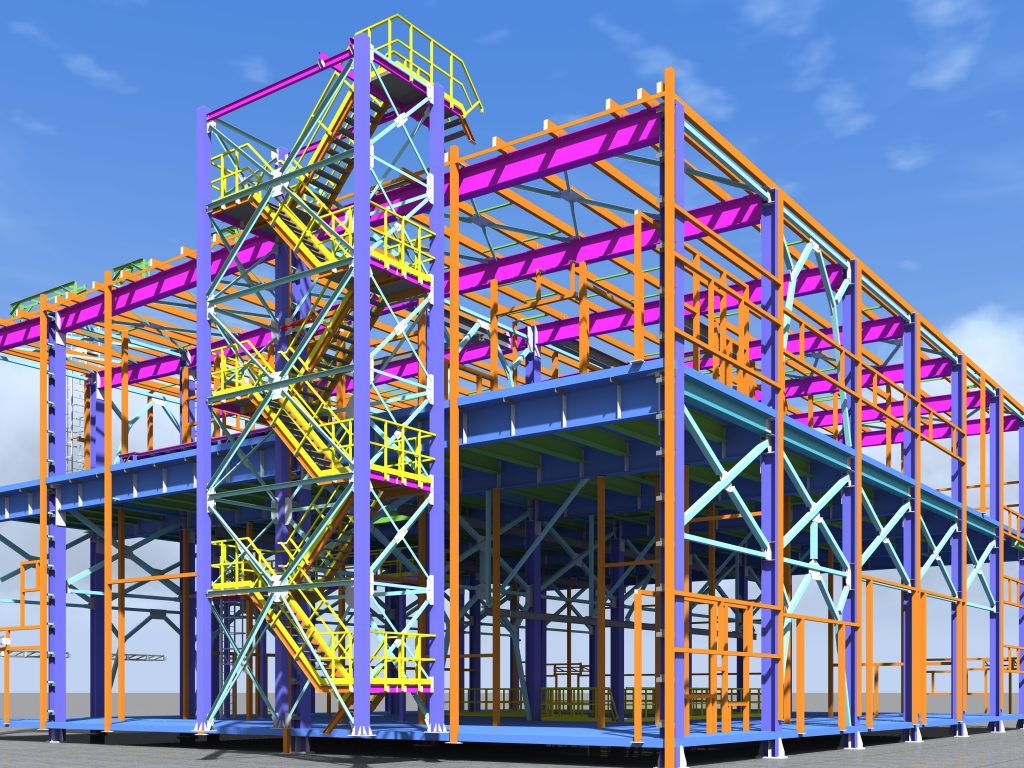
Structural BIM
Structural BIM (Building Information Modeling) refers to the use of BIM technology and processes specifically for structural engineering and design within a construction project. It focuses on creating a detailed digital representation of the structural elements and systems of a building or infrastructure project.
Structural BIM involves the development of a virtual 3D model that includes all structural components, such as beams, columns, slabs, walls, foundations, and structural connections. The model is created using specialized BIM software that allows structural engineers to design and analyze the structural elements in a digital environment.
Here are some key features and benefits of structural BIM:
BIM allows structural engineers to perform accurate analysis and design of the building’s structural elements. The digital model serves as the basis for structural calculations, load analysis, and the generation of design drawings.
Structural BIM enables the integration and coordination of structural elements with architectural and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems. Clash detection tools help identify and resolve conflicts or clashes between different building systems, ensuring that structural elements are properly coordinated.
Structural BIM allows structural engineers to visualize and explore the building’s structural components in a 3D environment. This helps in better understanding the structural behavior, connections, and interactions with other building elements.
BIM models facilitate the generation of accurate and coordinated structural documentation, including detailed drawings, schedules, and specifications. The digital model serves as a central source of information, ensuring consistency and reducing errors during the documentation process.
Structural BIM models can be used to extract quantities of structural elements for accurate cost estimation and procurement. This helps in cost planning and budgeting during the project lifecycle.
BIM enables structural engineers to perform advanced analysis and simulations, such as finite element analysis (FEA) and structural dynamics. This allows for the evaluation and optimization of structural performance, including factors like load distribution, deflection, and structural integrity.
Structural BIM facilitates collaboration among project stakeholders, including architects, MEP engineers, contractors, and owners. The digital model can be shared and accessed, fostering better communication and coordination throughout the project.
By utilizing structural BIM, structural engineers can create and manage a comprehensive digital representation of the building’s structural design. This improves design coordination, documentation accuracy, and overall project efficiency, leading to well-designed and structurally sound buildings.